From Code to Consumer: PAI’s Value Chain Analysis Illuminates Generative AI’s Key Players
![$hero_image['alt']](https://partnershiponai.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/open-FM-illuminate-key-players-1800x832-1.png)
Two years ago, Open AI changed the world with their release of ChatGPT, a chatbot and virtual assistant based on Large Language Models (LLMs). Although AI has been around for decades, this generative AI tool thrust AI into the technological spotlight for a wide audience. Used as a tool to assist in writing, answering questions, and making recommendations, ChatGPT is slowly becoming a staple in many people’s lives, fundamentally altering the way we think, learn, and work. Soon after its release, companies followed in the “AI Boom” and began releasing their own generative AI models such as Google’s Gemini, Meta’s Llama, etc.
Now we are on the precipice of yet another shift in AI technology as generative AI systems become integrated with the devices in our homes and pockets.
Apple’s integration of ChatGPT into Siri and Meta’s integration of Llama 3 into Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp have already made these generative AI systems part of our everyday lives. Just as checking your messages, calendar, and social media accounts is routine, using AI assistants will likely also become part of our day to day. This shift could make life easier, and our busy schedules more manageable. But this tech-enhanced future also comes with drawbacks and challenges. The incorporation of ChatGPT into Siri will change how we view and utilize AI assistants but as the technology becomes more capable and accessible, the potential for harm and unknown-unknowns may increase.
When these systems go beyond generating responses and providing information and move to acting on behalf of its users, they become “agents” or advanced digital assistants acting independently on behalf of humans. The unanticipated capabilities and results of these systems should give us pause. These advanced AI assistants or agents will be integrated into existing services and devices, representing the “domestication of generative AI” in our daily lives. These AI agents are built on foundation models by Application Developers, who play a critical role in the AI value chain. App developers are one of many actors in the value chain who hold certain responsibilities when it comes to governing their technology and how it’s used.
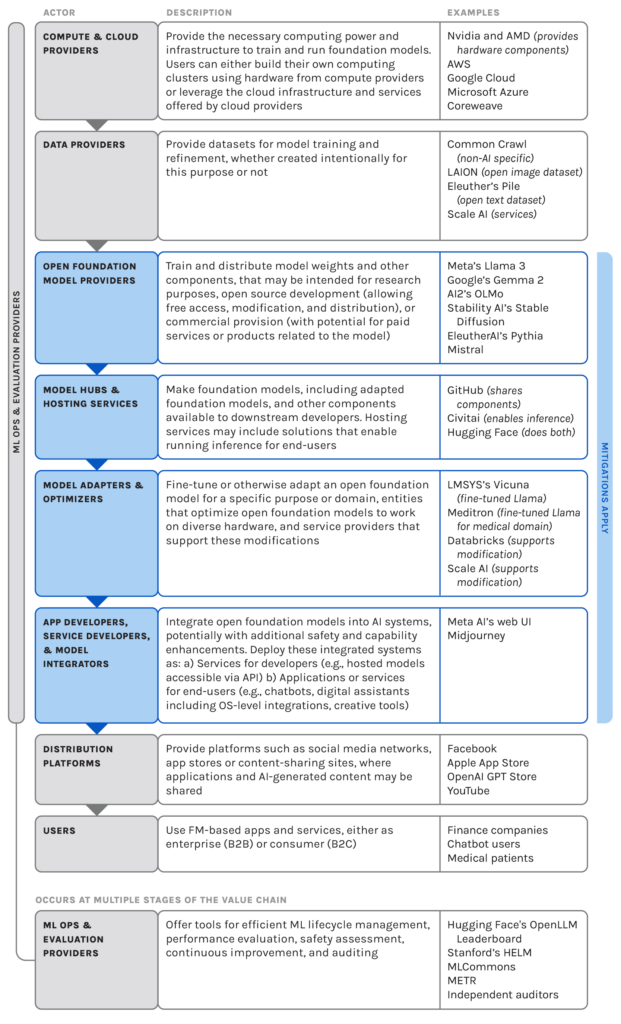
Examining what the AI value chain currently looks like will help us understand which actors play what roles, and when, how, or even if they should step in when problems arise. PAI’s new analysis of today’s open foundation models value chain provides a crucial baseline. As we look ahead to the rapid evolution of AI assistants and agents, understanding this baseline will help us anticipate and prepare for the shifts in the AI landscape that are likely to occur in the coming months and years.
Traditional regulatory approaches may be inadequate for this dynamic field – how do you regulate an ever changing landscape? It’s like trying to draw lines in a sand storm. To begin understanding how to regulate this space we must keep track of the rapidly changing AI value chain. As the AI ecosystem becomes more complex, with more actors and shifting roles, it’s imperative that we understand this intricate web in order to craft effective policy.
Although software and innovation is iterative, regulation is typically not. Regulating too quickly without understanding the technology and where it is headed can be detrimental to users and society. Understanding the stages of the AI value chain can help us predict where interventions can make a difference, and what risk mitigation strategies actors can implement. At PAI we have developed resources to help stakeholders navigate this complex landscape. Our recently released “Risk Mitigation Strategies for the Open Foundation Model Value Chain” resource provides a starting point for policymakers, industry, academia, and civil society leaders to discuss and address these emerging complexities. As our work in this area advances, so does our capability to respond to the growing uncertainties of AI and its increasing ubiquity in our lives.
Find more information on our new resource, which maps the landscape and risk mitigations for state-of-the-art open foundation models and the actors involved. This work complements our earlier ‘Guidance for Safe Foundation Model Deployment‘, which covers risk mitigation strategies for a broader range of foundation model capabilities and release scenarios. To stay up to date on how PAI is making an impact in this space sign up for our newsletter!



